‘Expensive and complicated’: Most rural hospitals no longer deliver babies
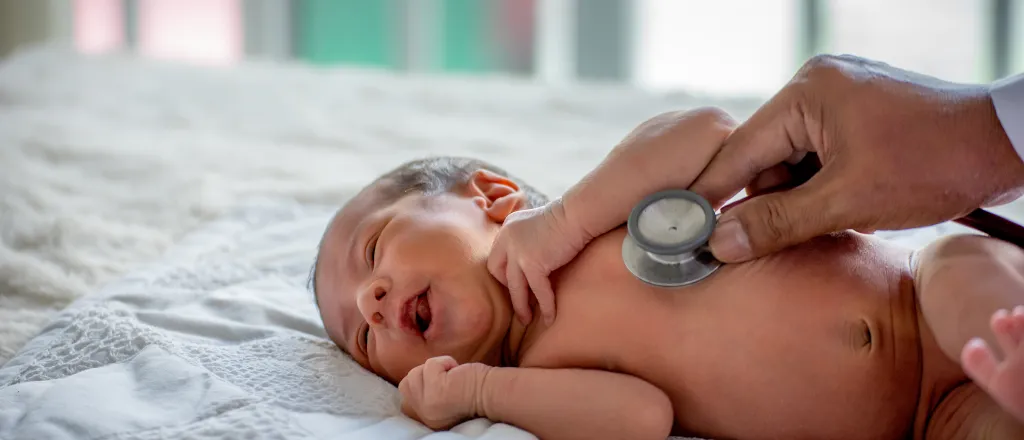
A mother prepares her infant son for bed. Since 2020, 36 states have lost at least one rural labor and delivery department. In rural counties, the loss of hospital-based obstetric care is associated with increases in births in hospital emergency rooms, less prenatal care and higher rates of babies being born too early. (Photo by John Moore/Getty Images)
Nine months after Monroe County Hospital in rural South Alabama closed its labor and delivery department in October 2023, Grove Hill Memorial Hospital in neighboring Clarke County also stopped delivering babies.
Both hospitals are located in an agricultural swath of the state that’s home to most of its poorest counties. Many residents of the region don’t even have a nearby emergency department.

© iStock - nevarpp
Stacey Gilchrist is a nurse and administrator who’s spent her 40-year career in Thomasville, a small town about 20 minutes north of Grove Hill. Thomasville’s hospital shut down entirely last September over financial difficulties. Thomasville Regional hadn’t had a labor and delivery unit for years, but women in labor still showed up at its ER when they knew they wouldn’t make it to the nearest delivering hospital.
“We had several close calls where people could not make it even to Grove Hill when they were delivering there,” Gilchrist told Stateline shortly after the Thomasville hospital closed. She recalled how Thomasville nurses worked to save the lives of a mother and baby who’d delivered early in their ER, as staff waited for neonatal specialists to arrive by ambulance from a distant delivering hospital.
“It would give you chills to see what all they had to do. They had to get inventive,” she said, but the mother and baby survived.
Now many families must drive more than an hour to reach the nearest birthing hospital.
Nationwide, most rural hospitals no longer offer obstetric services. Since the end of 2020, more than 100 rural hospitals have stopped delivering babies, according to a new report from the Center for Healthcare Quality & Payment Reform, a national policy center focused on solving health care issues through overhauling insurance payments. Fewer than 1,000 rural hospitals nationwide still have labor and delivery services.

iStock
Across the nation, two rural labor and delivery departments shut their doors every month on average, said Harold Miller, the center’s president and CEO.
“It’s the perfect storm,” Miller told Stateline. “The number of births are going down, everything is more expensive in rural areas, health insurance plans don’t cover the cost of births, and hospitals don’t have the resources to offset those losses because they’re losing money on other services, too.”
Staffing shortages, low Medicaid reimbursement payments and declining birth rates have contributed to the closures. Some states have responded by changing how Medicaid funds are spent, by allowing the opening of freestanding birth centers, or by encouraging urban-based obstetricians to open satellite clinics in rural areas.
Yet the losses continue. Thirty-six states have lost at least one rural labor and delivery unit since the end of 2020, according to the report. Sixteen have lost three or more. Indiana has lost 12, accounting for a third of its rural hospital labor and delivery units.
In rural counties the loss of hospital-based obstetric care is associated with increases in births in hospital emergency rooms, studies have found. The share of women without adequate prenatal care also increases in rural counties that lose hospital obstetric services.
And researchers have seen an increase in preterm births — when a baby is born three or more weeks early — following rural labor and delivery closures. Babies born too early have higher rates of death and disability.
Births are expensive
The decline in hospital-based maternity care has been decades in the making.
Traditionally, hospitals lose money on obstetrics. It costs more to maintain a labor and delivery department than a hospital gets paid by insurance to deliver a baby. This is especially true for rural hospitals, which see fewer births and therefore less revenue than urban areas.
“It is expensive and complicated for any hospital to have labor and delivery because it’s a 24/7 service,” said Miller.
A labor and delivery unit must always have certain staff available or on call, including a physician who can perform cesarean sections, nurses with obstetric training, and an anesthetist for C-sections and labor pain management.
You can’t subsidize a losing service when you don’t have profit coming in from other services.
– Harold Miller, president and CEO of the Center for Healthcare Quality & Payment Reform
“There’s a minimum fixed cost you incur [as a hospital] to have all of that, regardless of how many births there are,” Miller said.
In most cases, insurers don’t pay hospitals to maintain that standby capacity; they’re paid per birth. Hospitals cover their losses on obstetrics with revenue they get from more lucrative services.
For a larger urban hospital with thousands of births a year, the fixed costs might be manageable. For smaller rural hospitals, they’re much harder to justify. Some have had to jettison their obstetric services just to keep the doors open.
“You can’t subsidize a losing service when you don’t have profit coming in from other services,” Miller said.
And staffing is a persistent problem.
Harrison County Hospital in Corydon, Indiana, a small town on the border with Kentucky, ended its obstetric services in March after hospital leaders said they were unable to recruit an obstetric provider. It was the only delivering hospital in the county, averaging about 400 births a year.
And most providers don’t want to remain on call 24/7, a particular problem in rural regions that might have just one or two physicians trained in obstetrics. In many rural areas, family physicians with obstetrical training fill the role of both obstetricians and general practitioners.
Ripple effects
Even before Harrison County Hospital suspended its obstetrical services, some patients were already driving more than 30 minutes for care, the Indiana Capital Chronicle reported. The closure means the drive could be 50 minutes to reach a hospital with a labor and delivery department, or to see providers for prenatal visits.
Longer drive times can be risky, resulting in more scheduled inductions and C-sections because families are scared to risk going into labor naturally and then facing a harrowing hourlong drive to the hospital.
Having fewer labor and delivery units could further burden ambulance services already stretched thin in rural areas.
And hospitals often serve as a hub for other maternity-related services that help keep mothers and babies healthy.
“Other things we’ve seen in rural counties that have hospital-based OB care is that you’re more likely to have other supportive things, like maternal mental health support, postpartum groups, lactation support, access to doula care and midwifery services,” said Katy Kozhimannil, a professor at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health, whose research focuses in part on maternal health policy with a focus on rural communities.
State action
Medicaid, the state-federal public insurance for people with low incomes, pays for nearly half of all births in rural areas nationwide. And women who live in rural communities and small towns are more likely to be covered by Medicaid than women in metro areas.
Experts say one way to save rural labor and delivery in many places would be to bump up Medicaid payments.
As congressional Republicans debate President Donald Trump’s tax and spending plan, they’re considering which portions of Medicaid to slash to help pay for the bill’s tax cuts. Maternity services aren’t on the chopping block.
But if Congress reduces federal funding for some portions of Medicaid, states — and hospitals — will have to figure out how to offset that loss. The ripple effects could translate into less money for rural hospitals overall, meaning some may no longer be able to afford labor and delivery services.
“Cuts to Medicaid are going to be felt disproportionately in rural areas where Medicaid makes up a higher proportion of labor and delivery and for services in general,” Kozhimannil said. “It is a hugely important payer at rural hospitals, and for birth in particular.”
And though private insurers often pay more than Medicaid for birth services, Miller believes states shouldn’t let companies off the hook.
“The data shows that in many cases, commercial insurance plans operating in a state are not paying adequately for labor and delivery,” Miller said. “Hospitals will tell you it’s not just Medicaid; it’s also commercial insurance.”
He’d like to see state insurance regulators pressure private insurance to pay more. More than 40 percent of births in rural communities are covered by private insurance.
Yet there’s no one magic bullet that will fix every rural hospital’s bottom line, Miller said: “For every hospital I’ve talked to, it’s been a different set of circumstances.”