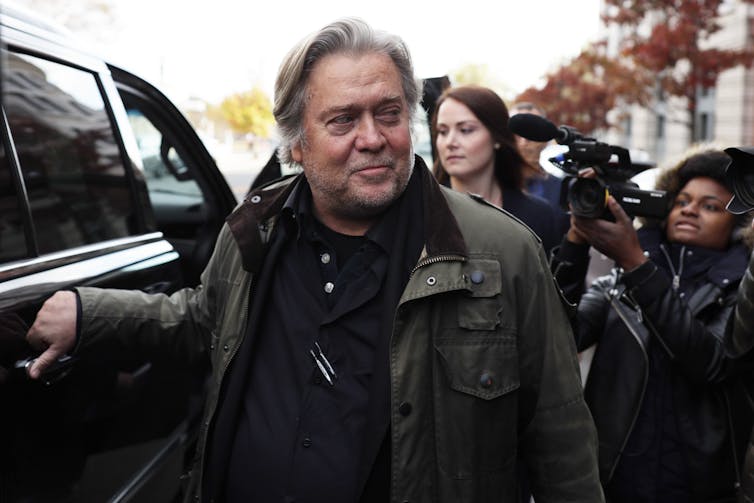
Steve Bannon is held in criminal contempt of Congress, pushing key question over presidential power to the courts

Jennifer Selin, University of Missouri-Columbia
Every president in history has refused to disclose information to Congress. These refusals are so commonplace that there is not even a comprehensive listing of how often they occur.
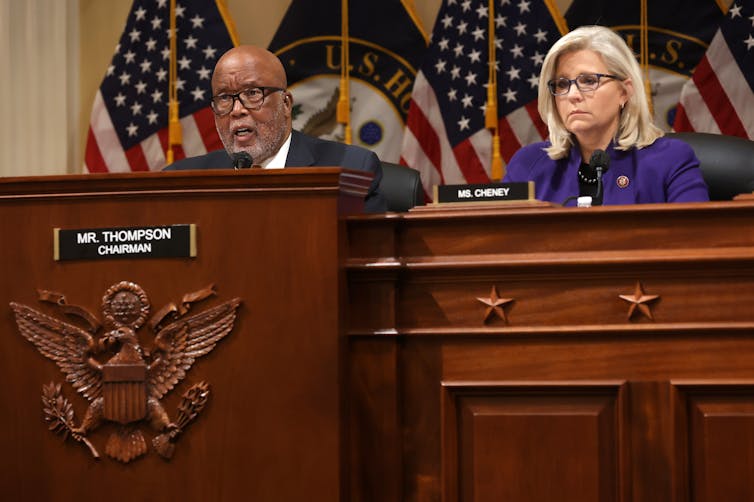
In just the latest incident, the House of Representatives voted to hold former Trump adviser Steve Bannon in contempt of Congress in mid-October 2021. At Trump’s request, Bannon defied a subpoena from the committee investigating the Capitol insurrection, refusing to testify.
The House vote captured the constant power struggle between presidents and Congress.
The recent eruption of this battle between the two branches of government over access to presidential information raises questions about the constitutional authority of Congress and how lawmakers acquire the information needed to hold the executive branch accountable in the U.S. system of separation of powers.

Power to investigate
No constitutional provision explicitly states that Congress has the authority to investigate problems or defects in the nation’s social, economic or political systems. But the legislature’s power to acquire information through investigation is an established part of representative democracy.
This is true regardless of the investigation’s end result or even whether critics accuse Congress of being partisan. As the Supreme Court put it in 1975, democratic governance means that some investigations may be nonproductive. In “times of political passion,” the court said, “dishonest or vindictive motives are readily attributed to legislative conduct and as readily believed.”
Over 200 years of Supreme Court precedent also recognizes that the fundamental right of Congress to investigate includes the power of subpoena, which compels testimony by an individual or requires them to produce evidence.
But the power of subpoena is of little value without the ability to enforce it. That mechanism is called contempt.
How contempt works
If a target of a congressional investigation refuses to comply with a subpoena, Congress can hold the individual in contempt. There are three forms of contempt – inherent, civil and criminal – each of which relies on a different branch of government for enforcement.
Congress has its own power to enforce a subpoena. However, to use that power, Congress has to conduct a trial and then find the individual in contempt. Because this process is lengthy and cumbersome, Congress has not used it since the 1930s.
Congress can also ask the courts to declare an individual in contempt. Known as civil contempt, this method requires a resolution authorizing a congressional committee or the House general counsel’s office to file a civil lawsuit. The courts then determine whether Congress has the right to the information it has demanded.
Congress used this power in the past three presidential administrations – Bush, Obama and Trump – to acquire information.
However, civil contempt is also slow moving. For example, Congress held Attorney General Eric Holder in civil contempt in 2012 for withholding information relating to Operation Fast and Furious, a Department of Justice policy that allowed certain illegal gun sales in order to track Mexican drug cartels. Congress eventually obtained some records, but it took seven years for courts to reach a settlement.
The last form of contempt relies on the executive branch – specifically the Department of Justice and U.S. attorneys – for enforcement. If someone refuses to testify or produce documents, a congressional committee can first cite the individual in criminal contempt and then ask its chamber of Congress to adopt a resolution affirming the committee’s decision. After that resolution, the Department of Justice and U.S. attorneys decide whether to pursue the matter in court.
Criminal contempt is what the House used in the Bannon case.
Bannon’s defiance
In June 2021, the House of Representatives established a select committee to investigate the facts and circumstances surrounding the Jan. 6 attack on the Capitol. As part of the select committee’s investigation, committee Chairman Bennie Thompson signed a subpoena requiring Bannon to produce documents by Oct. 7 and to appear for a deposition on Oct. 14.
In response to the subpoena, former President Trump instructed Bannon, his former aide, not to comply.
Bannon refused to provide a single document or appear for his deposition, citing Trump’s directive.
The select committee then issued a report recommending that the House hold Bannon in criminal contempt. On Oct. 21, the House agreed with the committee’s recommendation and adopted a resolution finding Bannon in contempt.
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi officially certified the contempt report and referred it to the Department of Justice this week. The department will now decide whether to prosecute the case.
Attorney General Merrick Garland said that the department “will apply the facts and the law” when making this decision.

The catch
While Bannon’s failure to comply with the congressional subpoena is striking, he needed to do so to challenge the subpoena.
To legally contest a congressional request for information, an individual first must refuse to comply and then, if held in criminal contempt, can provide a defense.
Bannon’s defense – and Trump’s instruction not to provide information to Congress – centers on the concept of executive privilege. Since President George Washington, executive officials have claimed the ability to withhold certain information that is fundamental to the operation of government. These claims relate to the idea that confidentiality encourages candor among presidents and their advisers when making important governmental decisions and policies.
In a letter to Bannon and three others under congressional investigation, Trump’s lawyer said they are protected from compelled disclosure “by the executive and other privileges, including among others the presidential communications, deliberative process, and attorney-client privileges.”
Presidents and their advisers have always interpreted executive privilege broadly. However, President Trump and his advisers have taken an even more expansive view than previous administrations.
My own research suggests that Trump and his advisers have asserted this privilege in at least 84 different federal cases. In contrast, in Obama’s first term, only 37 federal cases involved executive privilege claims. The claims in both administrations were made in a range of cases, from Freedom of Information Act lawsuits to lawsuits over agency actions.
Courts have recognized that cases over congressional access to information inevitably force the judiciary to side with one branch over the other. Yet, courts acknowledge the need to arbitrate disputes resulting from congressional investigations, particularly when those investigations could implicate presidential misconduct or criminal activity.
At least 14 presidential administrations have been the subject of investigations that required sitting or former presidents and their advisers to produce evidence. Legal disputes over these investigations have rarely made it to court.
But Bannon has made it clear that he will not cooperate with Congress until the judiciary steps in.
How the courts handle the matter will have implications for how Congress holds current and future presidential administrations accountable.
[Get The Conversation’s most important politics headlines, in our Politics Weekly newsletter.]![]()
Jennifer Selin, Kinder Institute Assistant Professor of Constitutional Democracy, University of Missouri-Columbia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.