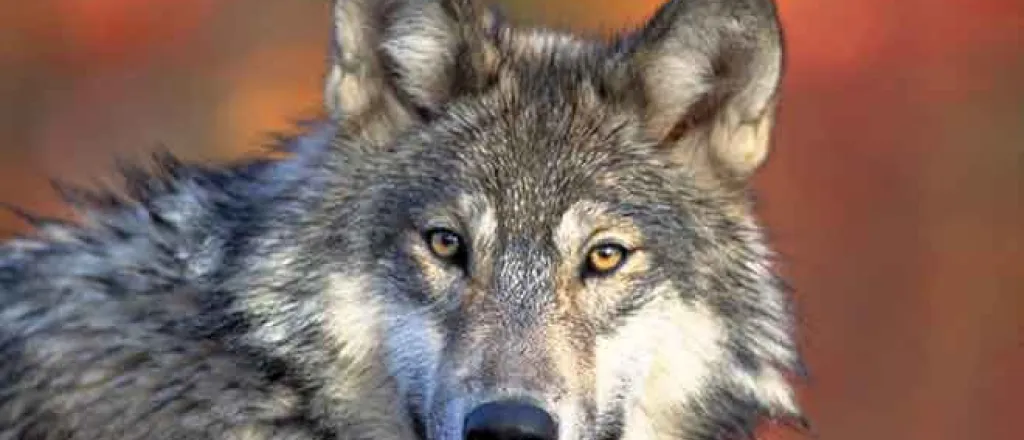
Colorado conservationists offer alternative plan for wolf reintroduction
(Colorado News Connection) A coalition of 14 conservation groups has unveiled an alternative proposal to help guide wolf reintroduction and recovery ahead of a Colorado Parks and Wildlife meeting this week in Edwards.
Lindsay Larris, wildlife program director, WildEarth Guardians, said the proposal focuses on the benefits and opportunities for fostering healthy wolf populations, in contrast to the agency's current emphasis on artificially limiting populations, and when and how wolves can be killed.
"There was a ballot measure that basically wants the public to be included in this process," Larris pointed out. "And we just have not seen enough of that thus far. And we're trying to put this plan forward to say this conservation alternative is probably what a lot of Coloradans would like to see."
The plan includes four science-based elements key to any wolf restoration effort: reintroduction areas, a population goal, management guidelines and compensation considerations for loss of livestock. In 2020, Colorado voters approved Proposition 114, a ballot measure to bring wolves back starting in 2023, and Colorado Parks and Wildlife has created two committees to compose a draft plan.
Conservation groups identified twelve optimal areas for the first round of reintroductions throughout the Western Slope, and their plan offers guidance as wolves enter the Front Range.
Dillon Hanson-Ahumada, Southern Rockies field representative for the Endangered Species Coalition, pointed to Yellowstone National Park, which began reintroducing wolves in 1995, and said Colorado could reap similar benefits.
"Everyone is familiar with the great reintroduction of wolves there, and how it benefited other species in the area," Hanson-Ahumada observed. "Now millions and millions of dollars go into the Yellowstone area every year because of the tourism that these wolves and other wildlife bring."
The plan provides compensation for loss of livestock, but gives incentives for ranchers to prevent conflict. Larris added there are proven nonlethal measures to keep wolves at bay, including the use of guard donkeys and llamas.
"Putting flaggery up, having range riders," Larris suggested. "We really want to really have a focus on avoiding the conflict in the first place. And that's why we really talk a lot of minimizing conflict techniques within the plan."